- A-
- A
- A+
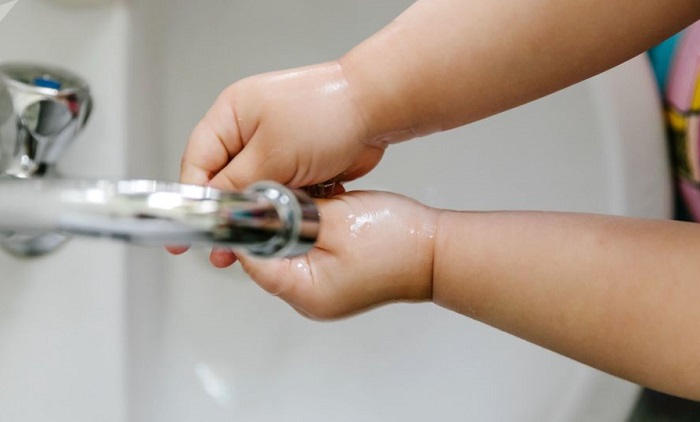
Today is the World Day of Hand Washing
Every year, more than 1.4 million children die from diarrhea or pneumonia worldwide, and infections account for 15 percent of newborn deaths. Washing hands with soap is an effective way to prevent these losses. Thus, it has been established that frequent washing of the hands of parents with soap contributes to the reduction of mortality among children at an early age from acute respiratory infections by 20 percent and from acute intestinal infections by 50 percent.
The United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) officially announced October 15 World Hand Day. The first such initiative was implemented in 2008 within the framework of the UN General Assembly Sanitation, when more than 120 million children from more than 70 countries washed their hands with soap. It also marked a significant increase in the involvement of countries and international organizations in the celebration of the World Clean Day. The purpose of large-scale actions organized on this day with the support of the UN in the whole world (special attention is paid to the countries of Asia, Africa and South America), - to attract public attention to the need for this simple, but very simple attitude.
Similar News
Links


 Elm TV
Elm TV
 Photo
Photo
 Video
Video