- A-
- A
- A+
Prosthetic Limbs, controlled by thought
Engineers at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab have developed a next-generation prosthetic: a robotic arm that has 26 joints, can curl up to 45 pounds and is controlled with a person’s mind just like a regular arm.
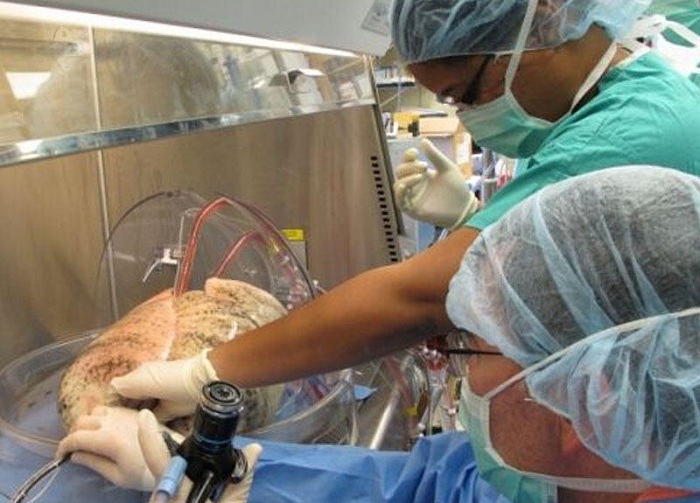
Researchers think the arm could help people like Les Baugh, who lost both arms at the shoulder after an electrical accident as a teenager. Now 59, Mr. Baugh recently underwent surgery at Johns Hopkins to remap the remaining nerves from his missing arms, allowing brain signals to be sent to the prosthetic.
Mr. Baugh’s custom socket can pick up brain signals to control the arms, known as Modular Prosthetic Limbs, or M.P.L., just by thinking about the movements.
Mike McLoughlin, the chief engineer of research and exploratory development at the lab, said that as the remapped nerves grew deeper, it was possible that Mr. Baugh would feel some sensation in his prostheses. Each arm has over 100 sensors, and other amputees who have had the same surgery reported being able to feel texture through the M.P.L.
Patients of varying disabilities have tested the arm in the lab and helped push the design forward.
The limb is modular, which means it can be broken off or built up to accommodate people with different needs — from a hand amputee to someone missing an entire arm. Quadriplegics or stroke survivors, who have lost the ability to move all or part of their bodies, can also use it as a surrogate arm.
But while the limb is fully functional, it still faces hurdles before making its way outside the lab. It will need approval from the Food and Drug Administration, which could mean a clinical trial.
Mr. McLoughlin also said the cost of the arm needed to be about a tenth of its current price to be viable in the marketplace. There are now about 10 fully functioning M.P.L.s, and each one costs an estimated $500,000.
Similar News
Links



 Elm TV
Elm TV
 Photo
Photo
 Video
Video